WAX Hyperion Full History when correctly configured and operated is a rock solid Antelope blockchain history solution, however there may exist a condition where blocks are indexed but are missing transactional data or blocks could be missing in their entirety.
Missing blocks can simply be identified through the API and can occur through a range of situations, mainly incorrectly starting and stopping the Hyperion indexer. The missing transactional data condition is a bit more obfuscated as the blocks are shown to be indexed, it has primarily been observed with older WAX node Antelope software in particular due to network fork events and an issue with the state-history plugin.
Providing a WAX Full History service without being 100% sure all history has been accurately captured is obviously a problem. Thankfully the Hyperion Team at EOS RIO have addressed this with the release of the Hyperion Index Repair Tool
This next sub-article in the series will cover the process of using the Hyperion Index Repair tool on a running Hyperion deployment or from a stand-alone Hyperion Indexer.
EOS RIO have an excellent Hyperion Documentation Repository including details on how to run their Hyperion Full History product, however this article will expand on their current documentation.
Once again this Technical How To series will cover some of EOS RIO’s same content and will add operational nuances from a practical stand point and our experience.
Learn more about EOS RIO Hyperion

This article has been updated to reflect the current Hyperion deployment in December 2024.
Repair WAX Hyperion Indexed Data
The Hyperion Index Repair Tool has been included in the Hyperion build package from v3.3.9–5 this version will have to built in order to access the repair functionality. The Repair Tool can however be used on a cluster from version v3.3.5 and above by using a stand-alone indexer with the newer software.
In this guide the process of running the Repair Tool on an operational Hyperion deployment will be covered as well as how to run the tool on a stand-alone indexer pointing to the operational Hyperion deployment.
Repair Tool Configuration
Ensure that you have upgraded to, or deployed Hyperion v3.3.9–5 or above. Please see our previous guides on Building WAX Hyperion Software.
The hyp-repair tool is located in the /hyperion-history-api directory.
The tool uses your existing connections.json configuration and requires that the control_port field is configured port 7002 is default as in the example below:
"chains": {
"wax": {
"name": "WAX Mainnet",
"chain_id": "1064487b3cd1a897ce03ae5b6a865651747e2e152090f99c1d19d44e01aea5a4",
"http": "https://wax.eosphere.io:443",
"ship": "wss://wax-ship.eosphere.io:443",
"WS_ROUTER_PORT": 7001,
"WS_ROUTER_HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"control_port": 7002Additionally as mentioned before it is possible to run the Repair Tool from a stand-alone indexer if for example you see an operational impact or if you have a v3.3.5 and above operational deployment that you don’t want to upgrade right now. In order to do this a new v3.3.9–5 Hyperion Indexer needs to be built and configured pointing to the existing Elasticsearch Cluster, this indexer is then run so as to allow access to the control port :7002 but without live indexing. Configure wax.config.json as below:
"indexer": {
"start_on": 0,
"stop_on": 0,
"live_reader": false,
"disable_reading": true,Essentially this indexer becomes a read and write gateway to the Elasticsearch Indices for the Repair Tool to work it’s magic.
Test the Configuration
Before running the repair check that the tool has access to the Hyperion Indexer:
> ./hyp-repair connect --host "ws://127.0.0.1:7002"
✅ Hyperion Indexer Online - ws://127.0.0.1:7002Running a Scan
Running a scan checks all indexed blocks for broken links on the chain. If a block is missing or when a block’s previous id is not the previous block id the tool will check the v1/chain/get_block to confirm if the version Indexed on Hyperion needs to be rewritten.
There are few ways to run the scan as below:
#Scan all blocks
> ./hyp-repair scan wax
# Scan a range
> ./hyp-repair scan wax --first 2 --last 10000000
# Scan specifying an output pathname
>./hyp-repair scan wax -o ./xyzIf a range isn’t specified the scan will start in reverse, from the last indexed block to the first indexed block in Elasticsearch.
If no output path is specified the scan output is saved in the ~/hyperion-history-api/.repair folder.
Verify the Scan
If missing or forked blocks are found a file will be created listing the discrepancies. View what was found as per below:
> ./hyp-repair view .repair/wax-4-250012558-forked-blocks.json
> ./hyp-repair view .repair/wax-4-250000861-missing-blocks.jsonOf course you may have no issues and in that case no file will be created.
Start the Repair
Now that it is known that there is missing data a repair can be run.
If a forked blocks file was created run the tool as below:
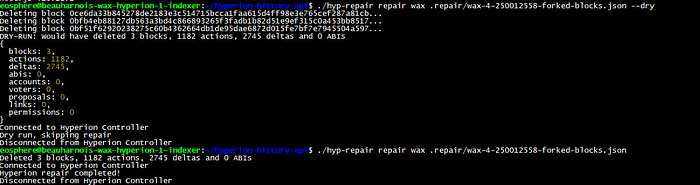
#Dry run to test the proposed repair
> ./hyp-repair repair wax .repair/wax-4-250012558-forked-blocks.json --dry
#Actual repair if the dry run looks good
> ./hyp-repair repair wax .repair/wax-4-250012558-forked-blocks.jsonIndex Repair will then delete these forked blocks and request the indexer to specifically fill these now missing blocks again.
If a missing blocks file was created run the tool as below:
> ./hyp-repair fill-missing wax .repair/wax-4-250000861-missing-blocks.jsonIt’s a good idea to then re-run the scan to ensure you have successfully fixed any undesirable missing data conditions and the Index Repair Tool has worked it’s magic.
These WAX Developer Technical Guides are created using source material from the EOSphere WAX Technical How To Series
Be sure to ask any questions in the EOSphere Telegram

