WAX Hyperion Full History is awesome for running lightning fast queries on historical indexed data, however certain dApps, Applications and specific use cases require a live view of indexed data. Hyperion is quite capable of providing this through a feature called streaming.
The Hyperion Streaming feature is quite simply enabled in the wax.config.json file and can be accessed and utilised using the EOS RIO Hyperion Stream Client.
A common issue encountered after enabling this streaming feature on a production WAX Hyperion Full History service is that it simply won’t work when situated behind a load balancer. The reason for this is that Hyperion streaming uses a websocket connection on a non standard port by default and ideally requires the load balancer to be configured and listening for websocket upgrade requests.
This next sub-article in the series will describe how to enable and configure Hyperion streaming using websockets on HAProxy.
EOS RIO have an excellent Hyperion Documentation Repository including details on how to run their Hyperion Full History product, however this article will expand on their current documentation.
Once again this Technical How To series will cover some of EOS RIO’s same content and will add operational nuances from a practical stand point and our experience.
Learn more about EOS RIO Hyperion

This article has been updated to reflect the current Hyperion deployment in December 2024.
WAX Hyperion Streaming with a WAX Load Balancer
Websockets create a full duplex connection between client and server over a single TCP connection which is utilised by the Hyperion streaming feature. In order to provide load balancing and redundancy of this streaming service, a reverse proxy that supports websockets is needed.
HAProxy has a very neat automated ability to upgrade an existing HTTP connection to a TCP websocket using Connection: Upgrade and Upgrade: websocket HTTP headers it can also be configured to simply recognise a specific URL that will point directly to the websocket server or streaming service in this case.
Once the websocket TCP tunnel connection is made, it will stay up until one of the nodes terminates or until the session timeout is reached. Below is a diagram I borrowed from HAPrroxy to visualise the setup flow.
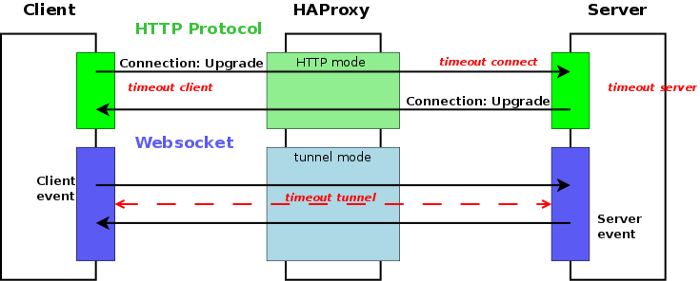
Websocket flow and timeouts of each phase
You can read more about Websockets Load Balancing with HAProxy on the HAProxy website.
In my research I also read a good article on troubleshooting Websocket/HAProxy timeouts, your mileage may vary when using State-History nodes but it may be advantageous to configure a specific tunnel timeout. Ours is set to 35 seconds in the HAProxy defaults section as below.
defaults
timeout tunnel 35000In this example HAProxy will be configured to recognise a websocket connection+upgrade header and direct these requests to a Hyperion streaming server, if your deployment has more than one Hyperion streaming API these requests will be load balanced.
Be sure to review "How to Set Up a Reliable WAX Load Balancer" for details on how to build and configure HAProxy in it’s entirety.
Configuration
In this example the goal is to:
- Enable streaming on the Hyperion API server
- Configure the HAProxy frontend to recognise traffic based on URL and Connect+Upgrade HTTP Header (frontend is a public IP and backend is a private LAN)
- Configure the frontend to route traffic to the appropriate backend Hyperion streaming API based on websocket traffic.
- Configure the front end to accept either websocket
ws:or websocket securewss:connections. Thewss:protocol establishes a WebSocket over an encrypted TLS connection, while thews:protocol uses an unencrypted connection. - Configure backend servers, load balance algorithm and thresholds
Hyperion Configuration
Streaming is enabled in the wax.config.json file as per below
> nano wax.config.json
"features": {
"streaming": {
"enable": true,
"traces": true,
"deltas": true
},By default the streaming websocket port is :1234 which is what we use but can be manually changed as below
> nano wax.config.json
"api":
"stream_port": 1234,
"stream_scroll_limit": -1,
"stream_scroll_batch": 500Once configured, restart the Hyperion Indexer and Hyperion API PM2 process
> cd ~/hyperion-history-api
> pm2 start --only wax-indexer --update-env
> pm2 start --only wax-api --update-envThe streaming service can be tested locally by running the below command
> curl 127.0.0.1:1234/stream/
{"code":0,"message":"Transport unknown"}HAProxy Configuration
HAProxy configuration is found in haproxy.cfg, follow the below to configure each section
> sudo nano /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgfrontend
Configure an access-list called wax_acl to recognise normal HTTP requests for your URL, in this case wax.eosphere.io. And then configure two access-lists one for recognising a connection upgrade request wax_con_upg_acl and one to recognise an upgrade to websocket request wax_ws_upg_acl.
frontend http-in
acl wax_acl hdr(host) -i wax.eosphere.io
acl wax_con_upg_acl hdr(Connection) -i upgrade
acl wax_ws_upg_acl hdr(Upgrade) -i websocket
##Alternatively a websocket specific URL rather than a dynamic upgrade can be used to point all traffic to your state-history servers##
acl wax_acl hdr(host) -i ws-wax.eosphere.ioBind the above access-list to a backend server group specifying the Hyperion streaming websocket and normal HTTP API’s server groups. In this example the following is configured.
- Normal v1 API queries are sent to the
wax_api_serversbackend - Websocket traffic is sent to the
wax_hyperion_streaming_serversbackend
use_backend wax_api_servers if wax_acl { path_beg /v1/chain }
use_backend wax_api_servers if wax_acl { path_beg /v1/node/get_supported_apis }
use_backend wax_hyperion_streaming_servers if wax_acl wax_con_upg_acl wax_ws_upg_aclIf you have configured your HAProxy to accept HTTPS on port :443 and provide SSL Offloading (please see "How to Set Up a Reliable WAX Load Balancer" for details) your reverse proxy will accept wss: as well as ws: connections.
backend
Configure the backend server groups to match your infrastructure and apply specific policies for each server group, in this case HTTP API servers and Hyperion streaming websocket servers.
The configuration below provides example servers and policy to match the above configuration. In particular the wax_hyperion_streaming_servers are configured to be checked if available (they will be marked as down and not used if unavailable) with a maximum of 200 connections specified.
backend wax_api_servers
balance roundrobin
default-server check maxconn 10000
server wax-pn-1 <PRIVATE LAN IP>:8888 cookie server1 weight 1
server wax-pn-2 <PRIVATE LAN IP>:8888 cookie server2 weight 1
server wax-pn-3 <PRIVATE LAN IP>:8888 cookie server3 weight 4
backend wax_hyperion_streaming_servers
balance leastconn
default-server check maxconn 200
server wax-hyperion-api-1 <PRIVATE LAN IP>:1234 cookie server1 weight 1
server wax-hyperion-api-2 <PRIVATE LAN IP>:1234 cookie server2 weight 1balance leastconn is used for the Hyperion streaming servers in this example as it seems to be better method to balance long lasting connections for our experience.
And that is it, your Hyperion streaming service is ready for public use.
Of course there are many of ways for you to setup websocket load balancing and resiliency for WAX services, the example in this article is how we are currently configured at EOSphere and will give you enough detail to be able to customise for your own deployment.
These WAX Developer Technical Guides are created using source material from the EOSphere WAX Technical How To Series
Be sure to ask any questions in the EOSphere Telegram

